Flex Rigid PCB Manufacturer Process
Rigid-Flex PCBs combine the advantages of rigid PCBs with the flexibility to fold or twist the board into the desired product shape. The result is a compact, lightweight, and efficient circuit board solution for your device design.
Flex PCBs can be produced with single, double or multi-layered boards. The layers are bonded together using thermal and pressure-based processes to form the flex circuit layer. The flex circuit is then inserted between two or more rigid sections of the PCB to form a hybrid board. The layers are then etched to create the desired circuit patterns and components. A copper plating process is used to provide electrical connectivity between the flex and rigid sections of the board.
To ensure the integrity of the flex rigid pcb manufacturer, it is important to have a good understanding of how it will be subjected to stress and strain during bending or folding. This is achieved through the careful design of the flex zones, as well as the selection and placement of components on both rigid and flex areas of the board. The layer stack-up must be optimized for both the rigid and flex zones, and must consider factors such as impedance control and thermal management.
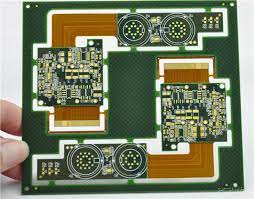
The Flex Rigid PCB Manufacturer Process and What You Should Know
When designing a flex PCB, it is important to consider the size and thickness of the pads and vias. Thicker pads can better resist stress cracking and have better performance when compared to thinner pads. Also, the pad shape should be carefully considered, as a square or rectangular shape will have better mechanical properties than an oval or circular shape. The choice of copper thickness also depends on the design requirements of the flex circuit.
The outer layers of the flex circuit are protected by a coverlay material, typically a polyimide film. This acts as a solder mask, protecting the non-soldered areas from environmental factors and accidental short circuits. The coverlay is then printed with the component identification, reference designators, and other markings required for the circuit assembly.
Once the outer layers have been patterned and etching is complete, holes are drilled into the rigid-flex PCB with precision drilling systems or techniques. The hole diameters are then plated with copper, which is chemically deposited to establish the required connections between the rigid and flex circuit layers. Once the plated copper has cooled, the photosensitive etch resist is stripped from the surface of the circuit board.
Finally, the flex circuit is laminated to the rigid-flex PCB. Any stiffeners required for the flex circuit are then applied, and the entire hybrid board is subjected to rigorous electrical testing to verify that the isolation, continuity, and quality meet the specified design parameters. This can be done with flying probe or grid test systems.